SURFACE TREATMENT
SURFACE TREATMENT
Aerospace Processing India Pvt Ltd (API), is a joint venture between Aequs and Magellan Aerospace. It provides innovative surface treatment solutions that are not readily available in India. It is the first, and only, third-party facility in India to be approved by both Airbus and Boeing.
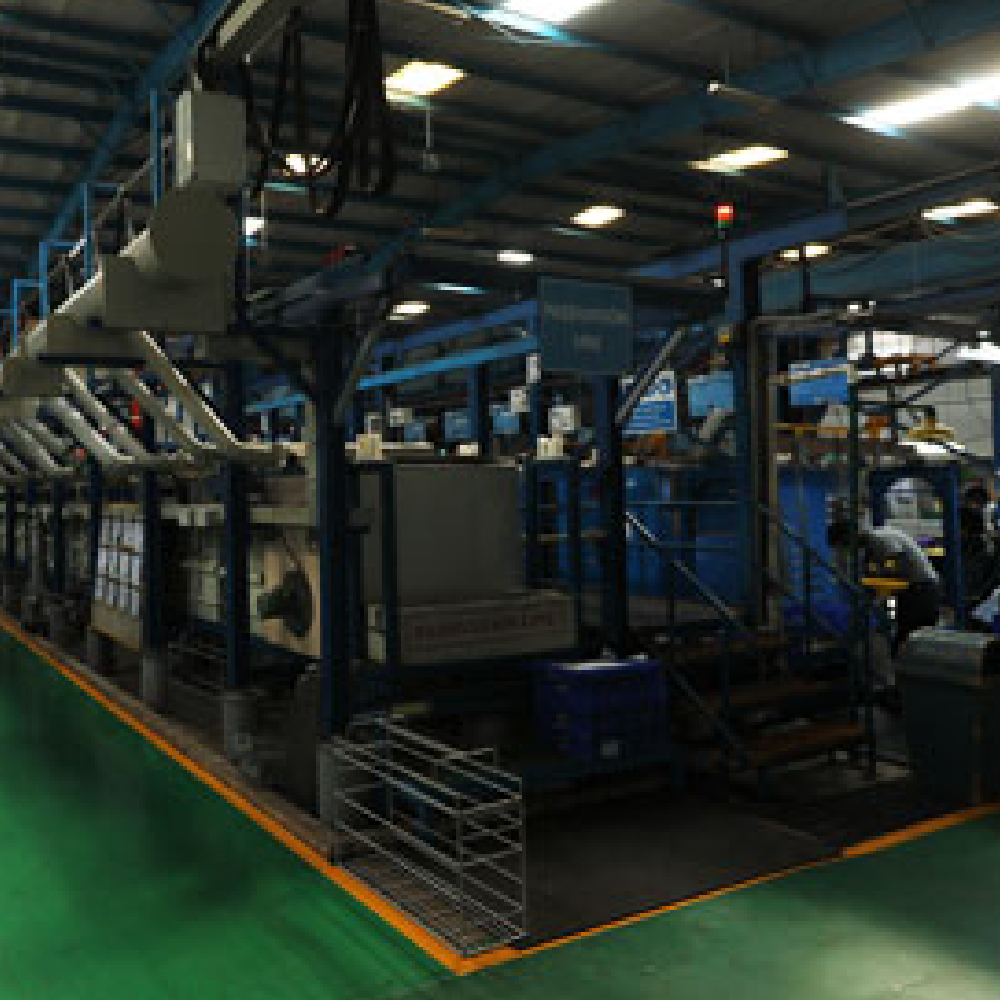

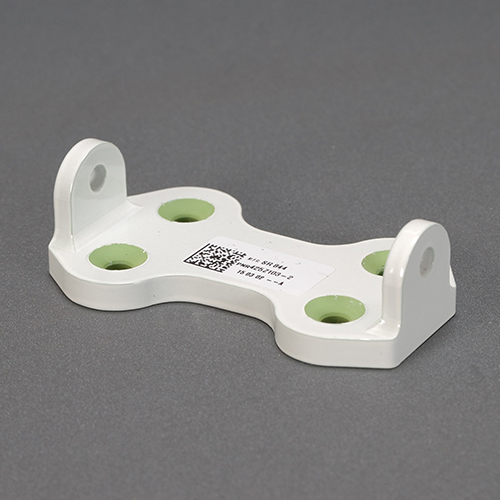
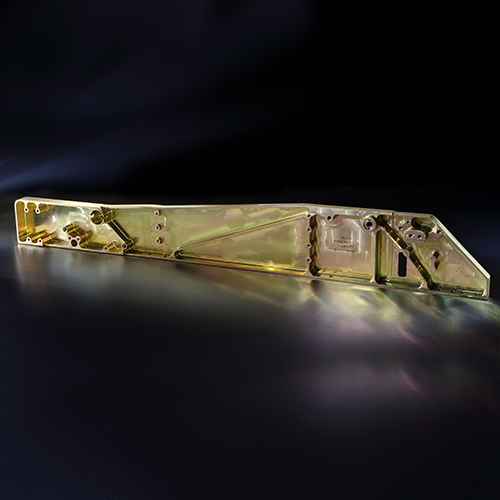
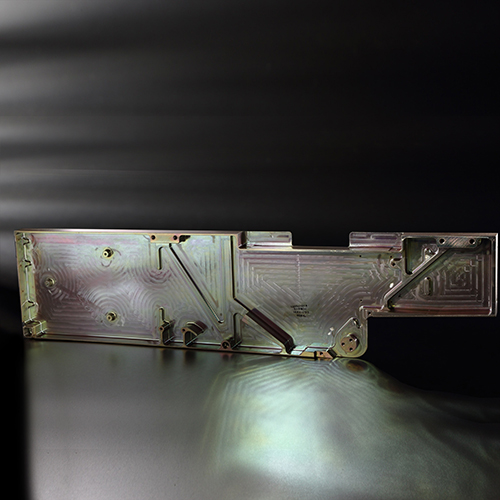
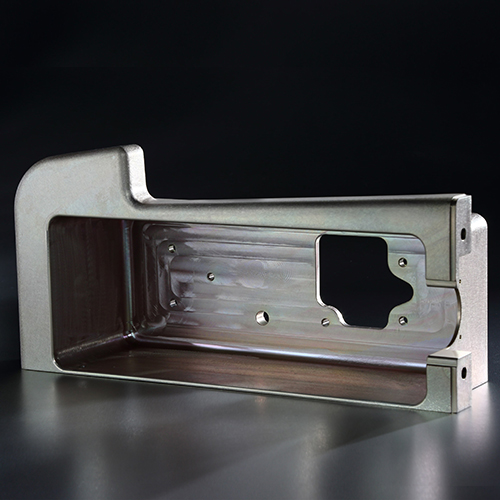
The surface treatment process is perhaps the most critical step to ensure quality, safety, and precision of parts for the aerospace industry. This is done by providing the parts with a physical shield that ensures protection against corrosion and moisture.
API is also the first unit in India to achieve NADCAP accreditation for Chemical Processing, Surface Enhancement, and Non-Destructive Testing (NDT). These are capabilities widely in demand across the aerospace industry. The unit is AS9100 Rev D and ISO 14001-2004 & BS OHSAS 18001:2007 certified.
India’s First 3rd Party Facility, approved by Airbus & Boeing
-
- NDT, Chemical Processing
- TSA/ Chromic/ Boric/ Sulphuric Anodize
- CAD Plating, Robotic Shot -Peen
- Al & Ti Etching, Alochrome & Alodine
- Prime, Paint, Molycoat, Part Marking
- Passivation & Salt Spray
Our Capabilities
NADCAP accredited cadmium and zinc nickel plating, robust and versatile metal coating, are widely accepted in the aerospace industry. A few ‘plating’ functions include corrosion inhibition, improving solderability, wearability, paint adhesion and IR reflectivity, reduce friction, alter conductivity, radiation shielding, among others. Cadmium plating is more toxic than zinc nickel plating and is being phased out. Additionally, zinc nickel plating is one of the best corrosion-resistant finishes available in the aerospace industry.
An electrochemical process that creates a thin aluminum oxide film electrically non-conductive. The active ingredient in type I anodizing is chromic acid, and it produces a thinner film than type II and type III anodizing (hard coat) with enhanced drawing and forming characteristics. Chromic acid anodizing is used for flight-critical aluminum components subjected to high stresses, such as landing gear.
TSA is an anodizing that results in a thin oxide layer with optimal adhesion properties and good corrosion resistance. The same is applied if strict requirements are imposed on corrosion resistance, and sulphuric anodizing is not an option due to the negative effects on fatigue strength. This process is mainly applied to aerospace components. Primarily, TSA is used as a pre-treatment before paint application.
NDT is the process of inspecting, testing, or evaluating materials, components or assemblies for discontinuities or differences in characteristics without destroying the serviceability of the part or system. It can be used to locate discrepancies in size, surface, and subsurface flaws. These non-destructive tests are often used to determine the physical properties of materials such as impact resistance, ductility, yield and ultimate tensile strength, fracture toughness and fatigue strength. NDT more effectively finds discontinuities and differences in material characteristics.
BSA is an anodizing that results in a thin oxide layer with optimal adhesion properties and good corrosion resistance. The same is applied if strict requirements are imposed on corrosion resistance, and sulphuric anodizing is not an option due to the negative effects on fatigue strength. The BSA process is mainly applied to aerospace components. Primarily, BSA is used as a pre-treatment before paint application.
Etching is carried out on parts/products to improve traceability, make the metal active and bring the grains on the surface. Marking is done through either chemical or non-chemical means like electrochemical etch marking, inkjet marking, marking with pens, and tagging onto Steel. Aluminum and aluminum alloy products and precise etching is done from mixed acids on titanium parts.
Anodizing is an electrolytic process through which a layer of oxide is produced to improve corrosion resistance, adhesion properties of bonding and wear and tear resistance. Anodizing can be done on highly corrosive metals, and based on the characteristic of the metal, different types of aqueous solutions are used.
To improve corrosion resistant property and aesthetic, moly coat and painting are done either using solvent-based paint or water-based paint. Application of paint can be made using a conventional spray or electrostatic or electrophoretic processes. Once the painting of the part/product is carried out, it is marked with a batch number for traceability.
Passivation and salt spray are standardized, and popular corrosion test methods used to check corrosion resistance of materials and surface coatings. Once the passivation is done using a light coat of protective material, it must undergo a corrosive attack then to evaluate the suitability of the coating for use as a protective finish. A salt spray test does this corrosive attack, and the appearance of corrosion products (rust) is evaluated after a pre-determined period.
NADCAP accredited Cadmium Plating is a robust and versatile metal coating process widely accepted in the Aerospace industry. Plating’s primary functions are: Decorate objects, corrosion inhibition, improve solderability, harden & improve wearability, reduce friction, improve paint adhesion, alter conductivity, improve IR reflectivity, and radiation shielding.
Imparting residual compressive stresses in the surface layers of metallic components is one of the ways to improve their fatigue strength characteristics. Shot peening is employed for imparting residual stresses using cold work by shooting tiny steel balls on the surface from a certain height with pressure to enhance the compressive strength of the material. In this process, compressive stress is induced to considerably reduce fatigue cracks during this operation.